Hybrid blockchains are an innovative blend of public and private blockchain technologies, designed to harness the best of both systems while avoiding their pitfalls. They therefore provide the perfect balance between the open, transparent nature of public blockchains, and the restricted, secure environment of private blockchains.
This article explains all corners of hybrid blockchains – exploring how they work, key features, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications – to ultimately give novice learners a better understanding over how this technology bridges the gap between public and private blockchains.
Let’s start with the basics…
Key Takeaways
- Definition: Hybrid blockchains combine the features of public and private blockchains.
- Key Features: Public Anonymity, Selective Transparency, Permissioned Access, Smart Contract Flexibility, Interoperability, and Scalability.
- How They Work: Hybrid Blockchains use a dual layer architecture comprised of a public and private layer.
- Real-World Examples: IBM Food Trust, XinFin Network, Ripple’s XRP Ledger, Dragonchain
What is a Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain merges the features of both public and private blockchains, meaning it’s designed to provide the best from both worlds…or in other words, the transparency and decentralization of public blockchains, combined with the security and control of private blockchains.
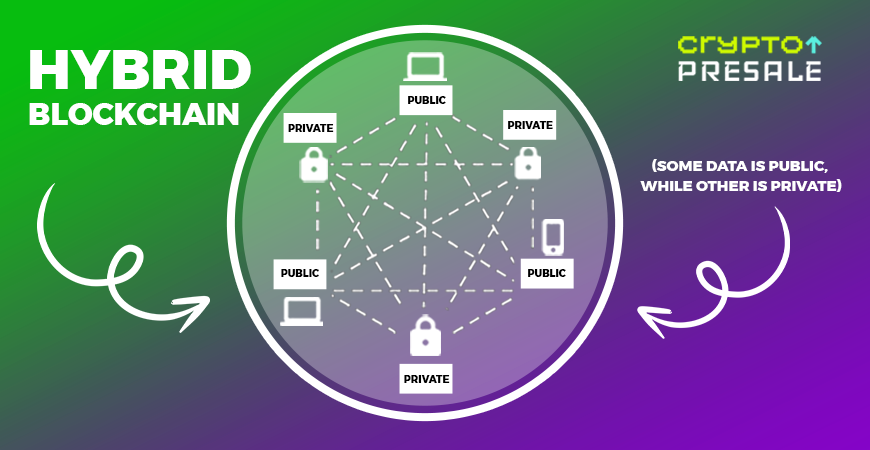
In contrast, anyone can participate in a public blockchain, be it validating transactions or accessing data. This openness ensures transparency and decentralization, but can also raise concerns over privacy and security. Conversely, private blockchains restrict access to a select group of participants, offering enhanced security and privacy but at the cost of reduced transparency and decentralization.
Hybrid blockchains address these challenges by allowing organizations to create customizable networks where certain data and transactions are made public, while others remain private and restricted to authorized participants. This flexible approach enables hybrid blockchains to meet various use case requirements, making them particularly appealing to industries that require both transparency and confidentiality.
The Unique Features of Hybrid Blockchains

Public Anonymity
One of the standout features of hybrid blockchains is public anonymity, which is achieved through participants being able to interact and conduct transactions without revealing their identities.
Not only does this ensure that the network remains decentralized and transparent while protecting user privacy, public anonymity is also crucial for applications where user identity needs to be protected, such as in financial transactions and public voting systems.
Selective Transparency
Hybrid blockchains enable selective transparency, allowing organizations to decide which data should be public and which should remain private.
This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses that need compliance with certain regulatory requirements for transparency, while maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive information. Selective transparency can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as permissioned access to specific data sets, or the use of encryption to protect private data.
Permissioned Access
Permissioned access is a defining feature of hybrid blockchains, allowing only authorized participants to access certain parts of the blockchain.
This feature ensures that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access, while still enabling public interactions. Permissioned access is typically managed through a system of permissions and roles, where different levels of access are granted based on the participant’s role and requirements.
Smart Contract Flexibility
Hybrid blockchains support the deployment of smart contracts on both public and private layers. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications, from public decentralized applications (DApps) to private business agreements.
Smart contracts on the public layer can facilitate open and transparent interactions, while those on the private layer can manage confidential transactions and agreements.
Interoperability
As is obvious, hybrid blockchains can interact with both private and public blockchain networks, enabling the transfer of data and assets across different blockchain environments. This capability enhances the scalability (more on this next) and efficiency of digital asset markets, allowing seamless integration with traditional financial systems.
Scalability
Hybrid blockchains are designed to be scalable, addressing one of the major challenges of public blockchains. By segregating public and private transactions, hybrid blockchains can manage large volumes of transactions more efficiently, which is essential for applications that require high throughput and fast transaction processing.
Enhanced Security
The combination of public and private elements in hybrid blockchains enhances overall security. This is because the dual security of a large, as well as the additional layers of security provided by private restrictions, ensure that hybrid blockchains can protect sensitive information while maintaining secure and robust.
Hybrid Blockchain VS Public and Private Blockchains
We’ve explored their differences in our separate article on Types of Blockchains, but let’s briefly revisit them here to clear up any misconceptions.
Public Blockchains:
- Accessibility:
- Open to anyone; participants do not need permission to join or view the blockchain.
- Security Model:
- Relies on widespread participation and complex consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) to secure the network.
- Use Cases:
- Best for applications where transparency and decentralization are paramount, such as cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
Private Blockchains:
- Control:
- Managed by a single organization or a consortium, providing centralized governance.
- Efficiency:
- Higher transaction speeds and lower latency due to fewer nodes and simpler consensus protocols.
- Use Cases:
- Ideal for internal enterprise solutions where privacy and control are crucial, such as in corporate data management and internal audits.
Hybrid Blockchains:
- Balanced Approach:
- Integrates the decentralization of public blockchains with the control of private blockchains, providing a tailored solution.
- Flexibility:
- Can cater to a wide range of applications needing both public engagement and private security, such as cross-industry collaborations and regulatory-compliant financial services.
- Optimized Performance:
- Achieves efficient transaction processing while maintaining the ability to handle public and private data as needed.
- Use Cases:
- Offers customizable compliance with regulations, making it suitable for industries that must adhere to strict data privacy laws.
Hybrid Blockchains vs Consortium Blockchains
Despite both being designed to offer specific benefits by combining elements of public and private blockchains, hybrid and consortium blockchains serve different purposes and use cases.
This is because consortium blockchains, also known as federated blockchains, are controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. In this model, the consensus process is managed by a pre-selected group of nodes, enhancing performance and security while limiting access to a trusted set of participants.
Consortium blockchains are therefore particularly useful for industry-specific applications where multiple organizations need to collaborate and share data securely, such as banking consortia and inter-company transactions.
Both blockchain types offer enhanced security, scalability, and control compared to purely public or private blockchains, however their suitability depends on the specific requirements of the use case – as whilst hybrid blockchains provide greater flexibility in managing public and private data, consortium blockchains offer a more controlled and collaborative environment among trusted parties.
How Do Hybrid Blockchains Work?
Nodes
Hybrid blockchains utilize a combination of public and private nodes to balance transparency with security. This means that nodes on a hybrid blockchain can openly participate in the network, validate transactions, and maintain a public ledger. At the same time, they can also restrict some participants from accessing sensitive data and private transactions.
Transactions
A hybrid blockchain offers the flexibility to tag each transaction individually, deciding whether it remains private or is recorded on the public ledger. This selective approach allows organizations to keep critical data confidential, while ensuring transparency for transactions where it is beneficial or required.
By balancing privacy and transparency on a transaction-by-transaction basis, hybrid blockchains provide a versatile solution that enhances trust in the system.
Smart Contracts
Like all types of blockchains, hybrid blockchains also use smart contracts, but with a unique twist. In a hybrid blockchain, smart contracts can be deployed on both public and private layers, providing flexibility in managing permissions and data access.
Interoperability
On top of that, the interoperability protocols in hybrid blockchains (such as Atomic Swaps, Interledger Protocol (ILP) and Hyperledger Cactus) enable seamless interaction between different blockchain networks. This interoperability ensures that data and assets can be transferred across various blockchain environments, enhancing the versatility and applicability of hybrid blockchain solutions.
Combining Public and Private Elements
The integration of public and private elements in hybrid blockchains is achieved through a dual-layer architecture:
- Public Layer: This layer handles transactions that need to be transparent and accessible to all participants. It ensures decentralization and maintains a public ledger for auditing and compliance purposes. Examples include public financial transactions and generic asset transfers.
- Private Layer: This layer is reserved for confidential transactions and sensitive data, which require restricted access. Only authorized participants can access this layer, ensuring the privacy and security of critical information. Examples include private business contracts and personal health records.
Consensus Mechanisms in Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains employ a variety of consensus mechanisms to validate transactions. For instance, a hybrid blockchain might use Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) on the public layer, while utilizing a more efficient and faster consensus algorithm like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) on the private layer. This combination allows the network to benefit from the security of public consensus mechanisms and the efficiency of private ones.
Examples of Data Handling and Transactions
In a hybrid blockchain, different types of data and transactions are managed according to their privacy requirements:
- Public Transactions: General transaction data, such as the transfer of assets or tokens, is recorded on the public layer, ensuring transparency and auditability. This can include public cryptocurrency transactions and open-source project logs.
- Private Transactions: Sensitive information, such as personal health records or proprietary business data, is stored and managed on the private layer, therefore only being accessible to authorized parties. Examples here include secure voting records and confidential business agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains offer numerous advantages, however they also come with certain challenges as well.
Advantages
- Scalability: Hybrid blockchains can handle large volumes of transactions efficiently by segregating public and private transactions.
- Security: The dual-layer architecture enhances security by combining the strengths of public and private blockchains.
- Flexibility: Organizations can customize the level of transparency and access according to their specific needs.
- Interoperability: Hybrid blockchains can interact with other blockchain networks, facilitating data and asset transfers across different environments.
- Privacy: Sensitive information can be protected through permissioned access, ensuring privacy while maintaining transparency where needed.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: The integration of public and private elements can make hybrid blockchains complex to design and manage.
- Potential for Centralization: The use of private elements may introduce centralization risks if not managed properly.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining a hybrid blockchain can be costly due to the need for advanced infrastructure and security measures.
Hybrid Blockchain Use Cases
Below are some unique ways hybrid blockchains can be deployed across different sectors.
Enterprise Services
Hybrid blockchains are ideal for developing both open-source software and enterprise-level solutions. In industries such as aviation, supply chain management, and healthcare, businesses can use hybrid blockchains to automate services and improve reliability, trust, and transparency for internal stakeholders and external customers. For example:
- Aviation: Airlines can use hybrid blockchains to manage maintenance records, ensuring they are transparent and immutable for regulatory compliance while keeping sensitive operational data private.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and medical research institutions can share anonymized patient data for research purposes on the public layer while keeping personal health records secure and private.
Hybrid IoT (Internet of Things)
Hybrid blockchains offer an efficient solution for managing IoT networks, which often face security vulnerabilities when using public blockchains. By leveraging hybrid blockchain technology, only authorized devices can be added to a private network, enhancing security while allowing certain information to be shared publicly as needed. For example:
- Smart Homes: Hybrid blockchains can manage smart home devices, ensuring that sensitive data such as security camera footage remains private while allowing non-sensitive data like energy usage statistics to be shared for analysis and optimization.
- Industrial IoT: Manufacturing plants can use hybrid blockchains to monitor and manage machinery, ensuring operational data is secure while sharing performance metrics with authorized service providers.
Global Trade and Finance
Hybrid blockchains are transforming the financial sector by offering a balanced solution that combines transparency and confidentiality.
For instance, a platform called XinFin is working on a hybrid blockchain model, integrating Ethereum for public transactions and Quorum for private, confidential operations. Here, XinFin aims to provide a comprehensive platform for global trade and finance, enhancing transaction efficiency and security (more on XinFin below).
Government
Governments are increasingly adopting blockchain technology for various applications, including voting systems, public identity databases, and the distribution of social and humanitarian aid.
Hybrid blockchains are particularly suitable here because they provide the necessary control, while enabling public access where appropriate. For example:
- Voting Systems: Governments can use hybrid blockchains to ensure the transparency and integrity of voting processes while keeping voter identities private.
- Public Services: Hybrid blockchains can manage public records and identity verification systems, ensuring data integrity and accessibility while protecting sensitive personal information.
Supply Chains
Supply chains can greatly benefit from the hybrid blockchain approach due to their complexity and need for both transparency and confidentiality. For example:
- IBM Food Trust: This initiative uses a hybrid blockchain to enhance the efficiency and transparency of the food supply chain. Read on for an extensive overview of this.
- Logistics Companies: Many logistics and transportation companies are adopting hybrid blockchains to track shipments, manage inventory, and streamline customs processes. The public layer can handle general shipment data while the private layer protects sensitive business information.
Real-World Hybrid Blockchain Examples
IBM Food Trust
IBM Food Trust is a prominent example of a hybrid blockchain in action. This platform connects various stakeholders in the food supply chain – such as farmers, processors, wholesalers, distributors, and retailers – through a permissioned, immutable ledger. This network enables real-time tracking and verification of products from farm to table, enhancing traceability and reducing fraud.
How It Works:
- Public Layer: Provides transparency by recording publicly accessible information about the origins and journey of food products. Consumers and regulators can verify the authenticity and safety of food items.
- Private Layer: Protects sensitive business data, such as proprietary supply chain processes and competitive information, accessible only to authorized participants.
Key Applications:
- Walmart actively participates in the network in order to improve food safety and reduce waste.
- In the coffee industry, Farmer Connect utilizes IBM Food Trust to allow consumers to trace the journey of their coffee. By scanning a QR code on the coffee package, consumers can access detailed information about the coffee’s origins, including the farmers who grew the beans, the processors, and the distributors involved. This system not only builds consumer trust but also supports sustainable farming practices by providing transparency about the product’s journey and its environmental impact.
XinFin (XDC Network)
XinFin’s XDC Network is a hybrid blockchain designed for global trade and finance. It combines the benefits of public and private blockchains to provide a secure, efficient, and scalable solution for financial transactions.
How It Works:
- Public Layer (Ethereum): Facilitates transparent transactions that can be audited and verified by all participants.
- Private Layer (Quorum): Manages confidential financial data and transactions, ensuring privacy and security for sensitive operations.
Key Applications:
- Impel, a fintech company utilizing XDC Network for ISO 20022 compliant financial messaging and cross-border payments, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional systems like SWIFT.
- Yodaplus utilizes XDC Network for secure multisig wallets and asset tokenization solutions, providing a decentralized way to manage digital transactions and tokenize physical assets.
Ripple’s XRP Ledger
Although primarily known as a public blockchain, Ripple’s XRP Ledger has the flexibility to integrate hybrid blockchain models by allowing financial institutions to use private nodes for secure and efficient cross-border transactions. This ensures the benefits of transparency in cross-border transaction validation while protecting sensitive financial data.
How It Works:
- Public Layer (RippleNet):
- RippleNet’s public layer facilitates transparent transactions that can be audited and verified by all participants. This ensures trust and transparency across the network, making it suitable for cross-border payments and other financial services.
- Private Layer (Ripple’s Permissioned Network):
- Confidential Transactions: The private layer manages confidential financial data and transactions, ensuring privacy and security for sensitive operations. Only authorized participants can access and verify transactions, providing an added layer of security for private financial dealings.
Key Applications:
- RippleNet utilizes the XRP Ledger to enable fast, cost-effective cross-border payments. Financial institutions can process transactions within seconds, reducing the reliance on traditional systems like SWIFT. For example, Santander, which is the UK’s leading financial services provider, utilizes RippleNet for same-day international transfers.
Dragonchain
Dragonchain is a hybrid blockchain platform developed by Disney. It is designed to support the development of secure and scalable blockchain applications for various industries.
How It Works:
- Public Layer: Ensures transparency and auditability of transactions and data.
- Private Layer: Allows businesses to keep sensitive information confidential, accessible only to authorized participants.
Key Applications:
- Den.social, a new social media platform, uses Dragonchain’s authentication systems and public key-based authentication necessary for Web3 integration, ensuring secure and decentralized user interactions
- Medek Health, a US-based software company has deployed Dragonchain for secure healthcare data management and telemedicine services. It provides privacy-focused solutions for managing patient data and ensures compliance with health regulations.
Are Hybrid Blockchains the Future?

Yes. Hybrid blockchain technology is increasingly seen as the future of blockchain due to its ability to provide a balanced approach to transparency, privacy, and scalability.
Recent expert analyses and trends suggest that hybrid blockchains will play a pivotal role in various sectors, driven by their flexibility and adaptability.
Adoption Trends:
- Enterprise Integration: Large corporations and industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and government services are adopting hybrid blockchains to streamline operations, enhance security, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- IoT and Smart Cities: The integration of hybrid blockchain with IoT devices is expected to grow significantly. Hybrid blockchains can secure IoT networks, manage data privacy, and support scalable applications. Smart cities, for example, can use hybrid blockchain to manage public services, ensuring data integrity and privacy for citizens.
Future Predictions:
- Vitalik Buterin, Co-founder of Ethereum: On numerous occasions, Vitalik has highlighted the potential of hybrid smart contracts and blockchain models to address scalability and privacy challenges in Decentralized Finance (DeFi). He suggests that combining on-chain and off-chain solutions can lead to more robust and versatile blockchain applications.
- Increased Interoperability: Experts predict that hybrid blockchains will become more interoperable with other blockchain frameworks and legacy systems. This will enable seamless data exchange and asset transfers across different platforms, enhancing the overall efficiency of blockchain ecosystems.
- Enhanced Privacy Solutions: With growing concerns about data privacy, hybrid blockchains are expected to incorporate advanced privacy-preserving technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multi-party computation. These innovations will allow hybrid blockchains to offer even stronger guarantees of privacy and security for sensitive data.
- Regulatory Compliance: As governments and regulatory bodies increasingly scrutinize blockchain applications, hybrid blockchains are well-positioned to meet compliance requirements. Their ability to provide both transparency and controlled access makes them suitable for applications that require regulatory oversight, such as financial services and healthcare.
- DeFi Expansion: The DeFi sector is expected to embrace hybrid blockchains to overcome current limitations related to scalability and security – as hybrid solutions can offer the necessary infrastructure to support complex financial products and services while maintaining user privacy and regulatory compliance.
Hybrid Blockchains – FAQs
What is the world’s first hybrid blockchain use case?
XinFin Network is the world’s first hybrid blockchain that enables smart contracts, ensures rapid transaction speed of up to 2000 transactions per second, and integrates KYC protocols for Masternodes. XinFin's hybrid blockchain combines the public Ethereum blockchain with the private Quorum blockchain.
This combination leverages the transparency and immutability of the public blockchain for data verification while using the private blockchain for faster, secure, and controlled transactions within the network. This hybrid blockchain uses a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism to enhance the scalability and efficiency of its blockchain network
What is the role of smart contracts in hybrid blockchains?
Smart contracts in hybrid blockchains automate transactions and enforce agreements transparently and securely. They can be deployed on both public and private layers, providing flexibility for various use cases.
How do hybrid blockchains support the Internet of Things (IoT) applications?
Hybrid blockchains can support IoT applications in more than one way. For instance, in a smart home system, sensitive data like access logs and user preferences can be stored on a private blockchain to ensure privacy, while critical events, such as security breaches or system updates, can be validated on a public blockchain for transparency and tamper-resistance.
Is XRP a hybrid blockchain?
No, Ripple’s XRP Ledger is primarily a public blockchain but incorporates elements of a hybrid model to enhance secure cross-border payments, providing flexibility for financial institutions to use private nodes for sensitive transactions.
 Never miss an Update!
Never miss an Update!  Top Cryptos to buy?
Top Cryptos to buy?







